Joint processing of visible (RGB) and near-infrared (NIR) images
has recently found some appealing applications, which make joint
capturing a pair of visible and NIR images an important problem.
In this paper, we propose a new method to design color filter arrays
(CFA) and demosaicing matrices for acquiring NIR and visible
images using a single sensor. The proposed method modifies
the optimum CFA algorithm proposed in [1] by taking advantage of
the NIR/visible correlation in the design process. Simulation results
show that by applying the proposed method, the quality of demosaiced
NIR and visible images is increased by about 1 dB in peak
signal-to-noise ratio over the results of the optimum CFA algorithm.
It is also shown that better visual quality can be obtained using the
proposed algorithm.
[1] Yue M. Lu, Clément Fredembach, Martin Vetterli, and Sabine Süsstrunk, "Designing color filter arrays for the joint capture of visible and near-infrared images," In Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, 2009.
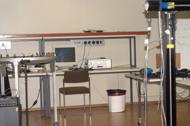
In each row from left to right:
1. The original visible image
2. The visible image demosaiced by the optimum CFA algorithm
3. The visible image demosaiced by the proposed algorithm
4. The original NIR image
5. The NIR image demosaiced by the optimum CFA algorithm
6. The NIR image demosaiced by the proposed algorithm
(Click on the images to see the full resolution)
| Original visible | Optimum CFA (visible) | Proposed algorithm (visible) | Original NIR | Optimum CFA (NIR) | Proposed algorithm (NIR) |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |  |  |